Value Validation Cycle: 5 Steps to Manage and Deliver Value-EN

Alonso Alvarez
- Business Analyisis
- Article
Anticipate Problems and Explain the Thought Process
Magic is fine in fiction, but in real life you usually don’t produce solutions by waving a wand and saying “Abra Cadabra”. In the world of business and projects we have two recipes that, even without magic, have seemingly magical results: anticipation and visualization (making ideas explicit).
- Anticipating problems does not automatically solve them, but it does allow us to prepare for when they occur, which includes mitigating or correcting their effect. Anticipating is about placing ourselves in the future to foresee potential changes and variations.
- Visualization is a way of exposing, ordering, and reviewing our thoughts and beliefs visually in order to organize and improve them.
A combination of the two is the opposite of improvisation and is a powerful planning tool to help us drive business value. Keep these two recipes in mind as we take a look at the Value Validation Cycle.
Managing the Value of the Organization with the Value Validation Cycle
I want to introduce you to a model that makes value management explicit, and thereby helps to anticipate the necessary steps to reach the goal(s). The “Value Validation Cycle” is a five-step cycle that helps articulate a vision of what we want to achieve and then helps us achieve it.
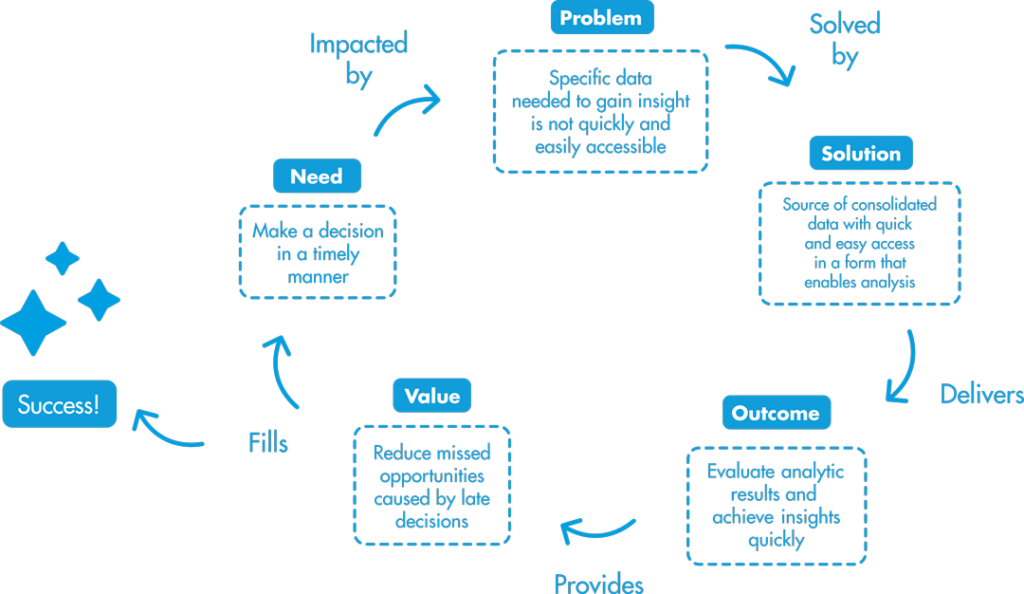
Use of the model is triggered by a need or problem.
- If that need is attainable, there is not much more to talk about. However, if it’s not, it is generally because it is impacted by a problem. There is something preventing the business need from being solved. Seen this way, a problem is a blockage to achieve the business objectives (the desired “success”).
- The problem or unmet need must be solved by a business solution. In an organization with multiple needs or problems, there are many potential solutions. You will have to determine which one has the most potential to offer the greatest value (more on that in a minute).
In the Value Validation cycle, the solution selected and implemented (by whatever means deemed appropriate – such as construction, acquisition, or modification) delivers an outcome that responds to the business need that triggered the cycle and ultimately provides business value.
The process can be repeated as many times as necessary until the business need that started the cycle has been achieved or has ceased to be of interest to the company.
The model is quite simple and easy to understand, but, unsurprisingly, there is quite a bit more under the surface.
Use the Business Drivers to Select the Most Suitable Solution
When considering the expected results to select the best solution, the model relies on the eight business drivers: increased revenue, reduced costs, improved customer service, better regulatory compliance and regulation, reduction of time-to-market, improvement of agility (understood as flexibility and speed), reduction of delivery time, and increased market reach.
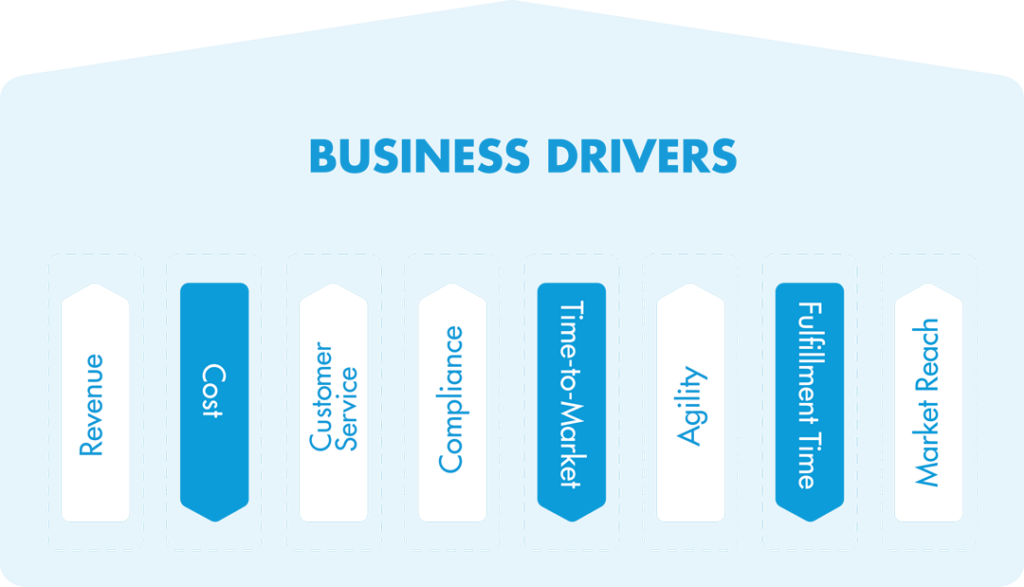
These drivers and other factors are complemented by the basic idea of forcing the identification of each stage of the validation cycle (the need, the problem, the solution, its results, and the value delivered), to reflect on them, and to design the appropriate strategies at each stage.
The Value Validation Cycle differentiates itself from other models by defining what the desired result looks like, what success looks like, and how to validate that success is achieved through the necessary mechanisms (metrics, indicators, or simply results achieved).
It’s still a simple idea that leans on the axes of anticipation and making ideas and actions explicit. This is not synonymous with planning, but with a cyclical (incremental, progressive) approach that has been proven to systematically address most recurring situations.
Next Steps: Achieve Your Organization’s Goals
The Value Validation Cycle leads to another tool that supports it and ties it all together – our Success Ladder. In the next article, I’ll walk you through the steps to take in our Success Ladder model to help you achieve your goals.
Learn and experience the Value Validation Cycle technique in our Establishing Business Value and KPIs course. During this class, we will complete the cycle by defining the appropriate indicators and metrics to validate the business solution.
— Alonso
